This Blog is an Open Resource Containing Links, Commentary, Back Ups, and Research Into a Wide Variety of Topics and How They Can Connect to the Modern World: Alchemy, Astronomy, Astrology, Archeoastrology, Egyptology, Etymology, Gematria, History, Isopsephy, Numerology, Esoteric Knowledge, Occult, Magic, Gnosticism, and Many More. This blog features materials protected by the Fair Use guidelines of Section 107 of the Copyright Act. All rights reserved to copyright owners.
Q the Brunes Star, Bases of Design by Walter Crane, Dynamic Symmetry, the Greek Vase by Jay Hambridge, and the Art of Composition: a Simple Application of Dynamic Symmetry by Michel Jacobs
This is a collection of archived research that has captured my interest into the Brunes Star, Bases of Design, Dynamic Symmetry in the Greek Vase, and the Art of Composition. Enjoy.

Dynamic Symmetry, the Greek Vase, Jay Hambridge
The Art of Composition: A Simple of Application of Dynamic Symmetry
Q Standing on the Shoulders of Giants

Wikipedia entry captured on 4.14.24
The phrase "standing on the shoulders of giants" is a metaphor which means "using the understanding gained by major thinkers who have gone before in order to make intellectual progress".
It is a metaphor of dwarfs standing on the shoulders of giants (Latin: nani gigantum humeris insidentes) and expresses the meaning of "discovering truth by building on previous discoveries". This concept has been dated to the 12th century and, according to John of Salisbury, is attributed to Bernard of Chartres. But its most familiar and popular expression occurs in a 1675 letter by Isaac Newton: "if I have seen further [than others], it is by standing on the shoulders of giants."
Early references- Middle Ages
An unknown attribution to Bernard of Chartres from John of Salisbury in 1159, John wrote in his Metalogicon: "Bernard of Chartres used to compare us to dwarfs perched on the shoulders of giants. He pointed out that we see more and farther than our predecessors, not because we have keener vision or greater height, but because we are lifted up and borne aloft on their gigantic stature." However, according to Umberto Eco, the most ancient attestation of the phrase dates back to Priscian cited by Guillaume de Conches.
According to medieval historian Richard William Southern, Bernard was comparing contemporary 12th century scholars to the ancient scholars of Greece and Rome. A similar conceit also appears in a contemporary work on church history by Ordericus Vitalis.
[The phrase] sums up the quality of the cathedral schools in the history of learning, and indeed characterizes the age which opened with Gerbert (950–1003) and Fulbert (960–1028) and closed in the first quarter of the 12th century with Peter Abelard. [The phrase] is not a great claim; neither, however, is it an example of abasement before the shrine of antiquity. It is a very shrewd and just remark, and the important and original point was the dwarf could see a little further than the giant. That this was possible was above all due to the cathedral schools with their lack of a well-rooted tradition and their freedom from a clearly defined routine of study.
Religious texts

An illustration of New Testament evangelists on the shoulders of Old Testament prophets, looking up at the Messiah (from the south rose window of Chartres Cathedral)
The visual image (from Bernard of Chartres) appears in the stained glass of the south transept of Chartres Cathedral. The tall windows under the rose window show the four major prophets of the Hebrew Bible (Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel, and Daniel) as gigantic figures, and the four New Testament evangelists (Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John) as ordinary-size people sitting on their shoulders. The evangelists, though smaller, "see more" than the huge prophets (since they saw the Messiah about whom the prophets spoke).
The phrase also appears in the works of the Jewish tosaphist Isaiah di Trani (c. 1180 – c. 1250):[9]
Should Joshua the son of Nun endorse a mistaken position, I would reject it out of hand, I do not hesitate to express my opinion, regarding such matters in accordance with the modicum of intelligence allotted to me. I was never arrogant claiming "My Wisdom served me well". Instead I applied to myself the parable of the philosophers. For I heard the following from the philosophers, The wisest of the philosophers was asked: "We admit that our predecessors were wiser than we. At the same time we criticize their comments, often rejecting them and claiming that the truth rests with us. How is this possible?" The wise philosopher responded: "Who sees further a dwarf or a giant? Surely a giant for his eyes are situated at a higher level than those of the dwarf. But if the dwarf is placed on the shoulders of the giant who sees further? ... So too we are dwarfs astride the shoulders of giants. We master their wisdom and move beyond it. Due to their wisdom we grow wise and are able to say all that we say, but not because we are greater than they.
Early modern and modern references - Isaac Newton
The quote is most often attributed to Sir Isaac Newton in a letter to his rival, Robert Hooke Isaac Newton remarked in a letter to his rival Robert Hooke dated 5 February 1675:
What Des-Cartes [sic] did was a good step. You have added much several ways, [and] especially in taking the colours of thin plates into philosophical consideration. If I have seen further it is by standing on the shoulders of Giants.
This has recently been interpreted by a few writers as a sarcastic remark directed at Hooke's appearance. Although Hooke was not of particularly short stature, he was of slight build and had been afflicted from his youth with a severe kyphosis.
Others
Cedalion on Orion's shoulders in a 1658 painting by Nicolas Poussin
Diego de Estella took up the quotation in the 16th century; by the 17th century it had become commonplace. Robert Burton, in the second edition of The Anatomy of Melancholy (1624), quotes Stella thus:
I say with Didacus Stella, a dwarf standing on the shoulders of a giant may see farther than a giant himself.
Later editors of Burton misattributed the quotation to Lucan; in their hands Burton's attribution Didacus Stella, in luc 10, tom. ii "Didacus on the Gospel of Luke, chapter 10; volume 2" became a reference to Lucan's Pharsalia 2.10. No reference or allusion to the quotation is found there.
In 1634, Marin Mersenne quoted the expression in his Questions harmoniques:
... comme l'on dit, il est bien facile, [and] mesme necessaire de voir plus loin que nos devanciers, lors que nous sommes montez sur leur espaules ...
Blaise Pascal, in the "Preface to the Treatise on the Vacuum" expresses the same idea, without talking about shoulders, but rather about the knowledge handed down to us by the ancients as steps that allow us to climb higher and see farther than they could:
C'est de cette façon que l'on peut aujourd'hui prendre d'autres sentiments et de nouvelles opinions sans mépris et sans ingratitude, puisque les premières connaissances qu'ils nous ont données ont servi de degrés aux nôtres, et que dans ces avantages nous leur sommes redevables de l'ascendant que nous avons sur eux; parce que s'étant élevés jusqu'à un certain degré où ils nous ont portés, le moindre effort nous fait monter plus haut, et avec moins de peine et moins de gloire nous nous trouvons au-dessus d'eux. C'est de là que nous pouvons découvrir des choses qu'il leur était impossible d'apercevoir. Notre vue a plus d'étendue; et, quoiqu'ils connussent aussi bien que nous tout ce qu'ils pouvaient remarquer de la nature, ils n'en connaissaient pas tant néanmoins, et nous voyons plus qu'eux.
Added Google translation, not in Wikipedia entry:
It is in this way that we can today take other feelings and new opinions without contempt and without ingratitude, since the first knowledge they gave us served as degrees to ours, and that in these advantages we are indebted to them for the ascendancy we have over them; because having risen to a certain degree to which they have carried us, the slightest effort makes us rise higher, and with less difficulty and less glory we find ourselves above them. This is where we can discover things that were impossible for them to see. Our view has more scope; and, although they knew as well as we do everything they could observe about nature, they nevertheless did not know so much, and we see more than they.
Later in the 17th century, George Herbert, in his Jacula Prudentum (1651), wrote "A dwarf on a giant's shoulders sees farther of the two."
Samuel Taylor Coleridge, in The Friend (1828), wrote:
The dwarf sees farther than the giant, when he has the giant's shoulder to mount on.
Against this notion, Friedrich Nietzsche argues that a dwarf (the academic scholar) brings even the most sublime heights down to his level of understanding. In the section of Thus Spoke Zarathustra (1882) entitled "On the Vision and the Riddle", Zarathustra climbs to great heights with a dwarf on his shoulders to show him his greatest thought. Once there however, the dwarf fails to understand the profundity of the vision and Zarathustra reproaches him for "making things too easy on [him]self." If there is to be anything resembling "progress" in the history of philosophy, Nietzsche in "Philosophy in the Tragic Age of the Greeks" (1873) writes, it can only come from those rare giants among men, "each giant calling to his brother through the desolate intervals of time", an idea he got from Schopenhauer's work in Der handschriftliche Nachlass.


Q the Secrets of Leonardo's Sacred Geometry, Writer of Fables and Short Stories

Leonardo was not only the brilliant painter, sculptor, architect, scientist, musician known all over the world, but he was also a writer of fairy tales. Short stories, scattered in various manuscripts and writings in the last decade of the fifteenth century, when Leonardo worked at the court of Ludovico il Moro. Inspired by typical themes of classic fairy tales, Leonardo's stories are characterized by having as protagonists not so much large animals, men and divinities, but rather plants, objects and small animals ignored by ancient fables, such as the spider or the butterfly. The attribution of human characteristics to simple tools, plants or inanimate objects is also innovative, which raises the bold fire, the superb cedar or the arrogant razor to the protagonists. The relationship between man and Nature is the leitmotif of all fairy tales, which is articulated according to four main themes: the need to remain in one's own state, with the suggestion of remaining within the limits imposed by Nature; the presumption punished, with the condemnation of those who exceed these limits; the criticism of complaining and excess, with the punishment of those who want a condition different from their own ...-- If you love great geniuses this book is for you.Leonardo da Vinci was not only the genius and innovator known for artistic works and futuristic machines. He was also a storyteller of fables and legends, full of wit and moral commitment. The true character of his stories is nature in its elements: water, fire, earth, air. Animals have life, thought and even the gift of speech. This volume collects stories suitable for children and adults, for a first encounter with the greatest genius in history. -Translated to try to remain as faithful as possible to Leonardo's way of writing and thinking.- If you want to start thinking like the greatest genius of the Renaissance, This book is for you!
Not only did Leonardo write with a special kind of shorthand that he invented himself, he also mirrored his writing, starting at the right side of the page and moving to the left. Only when he was writing something intended for other people did he write in the normal direction.
Mirror writing, Museum of Science, Boston

Linear Perspective Study For the Adoration ofthe Magi

Robert Edward Grant - New Discovery Inside the Great Pyramids King Chamber
Flipped horizontally, 50% opacity.



Q Art and Geometry in the Enneads of Plotinus and Their Arabic Adaptation, Polygons in Traditional Art and More
A short compilation of a few of my favorite lectures from the King's Foundation School of Traditional Arts.
Some screenshots and parts of the transcript from the above video:

Definitions
...Geometry of course, numbers represented as space. Right? And the word polygon itself, literally: "many knees". The greek term for what we call an angle, they called knee. You know, I just love how the Greeks and others used parts of the human body to associate with parts of, let's say, pottery. There's the mouth, the lip, the neck, the shoulder, the body, the belly, the foot, I like that the Greeks and others humanized it like that...

Regular Polygons
...Each regular polygon describes a different proportioning system, logically. And also interestingly a different symbol system. It's number symbolism around the world. Not exactly identical in all places, but there are great, great similarities. For example, the number seven...
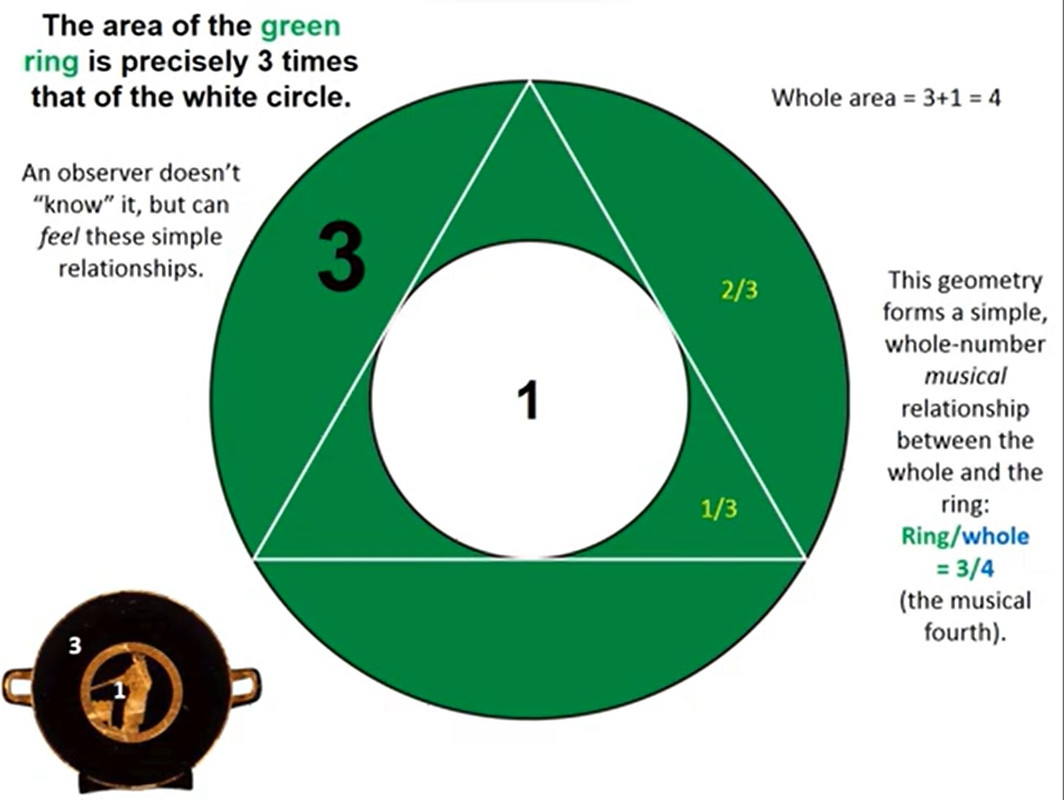
(Not mentioned in the video, but polygonal shapes seem to be "hidden" (or maybe just invisible) references to the Kabbalistic Tree of Life and/or references to the specific patterns of planetary motions in the sky as observed from earth.)



Commemorative Foundation Brick
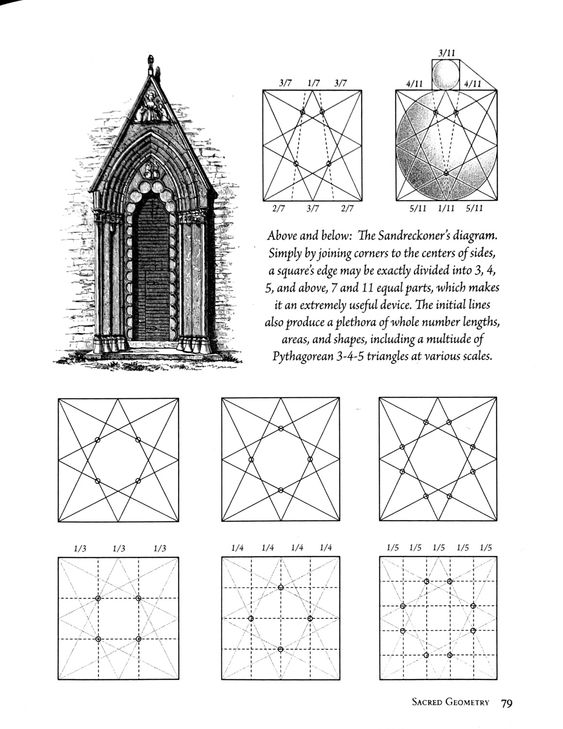
...What geometry explains this line (the base)? Tada. It's pentagonal...Symbolism for five, of course, has to do with life, living, the five of the hand, the five petal flowers and the appearance of the golden ratio in living forms,...the golden rectangle...

Talisman
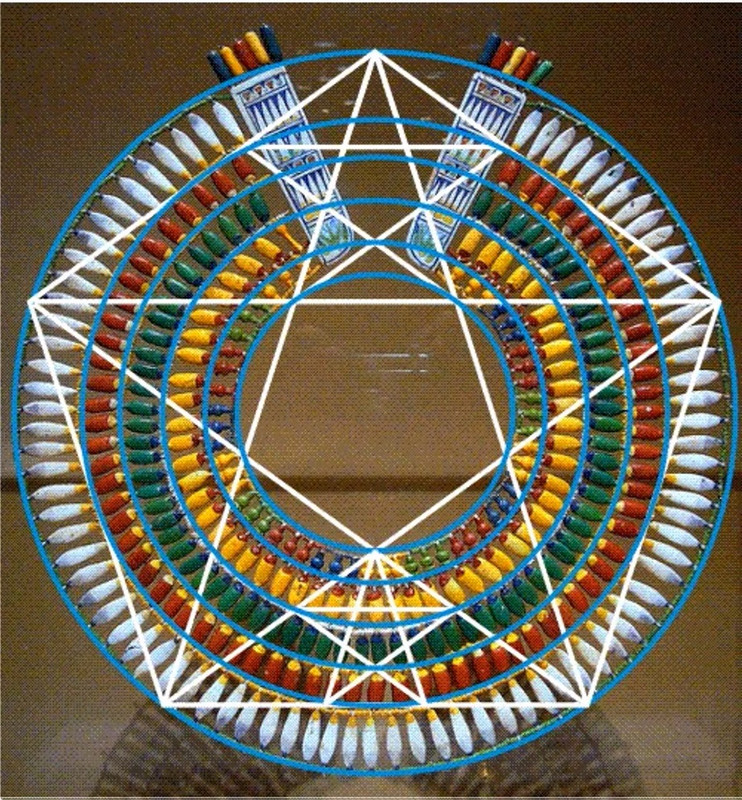
...Now we can assume that if the Egyptians are maintaining harmony here, how did they do it?... Well, since we're on the number five, let's put a circle around the whole and you can see the crossings of the pentagram imply this blue circle which shows the relationship now between the outer and the inner. And by the way, I might add, with the five pointed star in a circle or a circle with a center and five rays, any type/different depiction of the five is a very, very important Egyptian glyph, signifies the duat...which is translated as "underworld".

Nemus (sic) headress
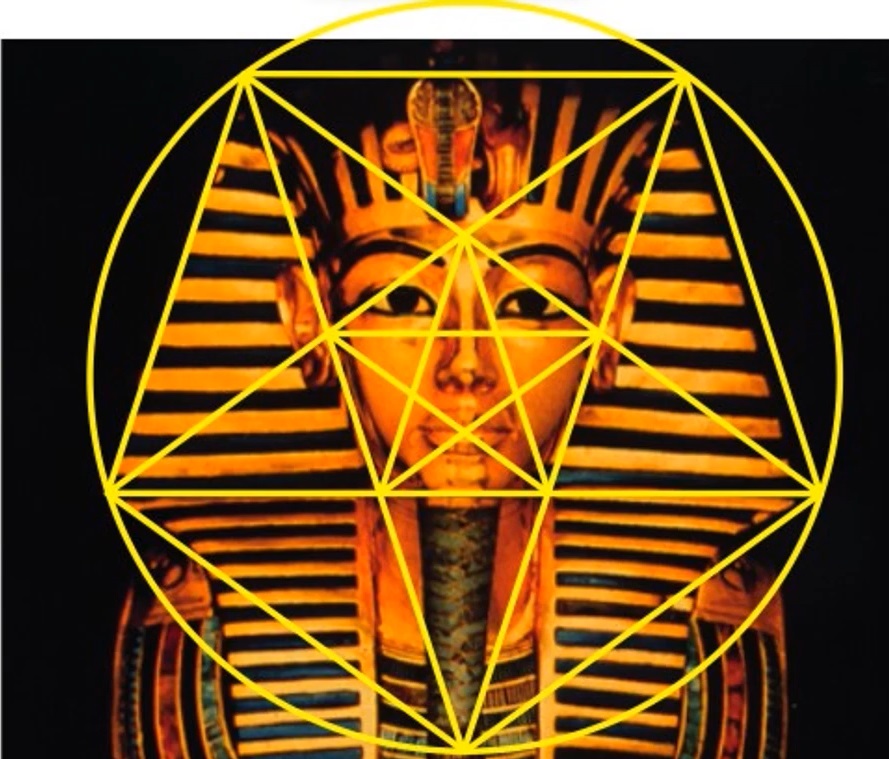
...ah, the famous King Tut, Nemes headress, OK? Now this photograph was taken off a little bit to the right so the match won't be quite precise but I think you can see that the angles will be perfectly fine. See what I've done is inscribe a pentagon (downward pointing pentagon), around a circle containing a whole scene. You see how it comes down to near the base of the beard and his chin and so forth and another pentagram inscribed within this pentagon places the nose at the precise center. And that's part of the Egyptian symbolism of the idea of the breath of life. Ok? Maybe you know the opening of the mouth ceremony in Egyptian art in the process the priest puts an oddly shaped stick up to the initiate's nose to breathe, to give him the breath of life. And interestingly enough that oddly shaped stick, which I don't have depicted here, at the very end is a piece of meteor, meteoric iron. That's the only way that the Egyptian's got their iron. There was no mining, they didn't import it. They only got their iron from meteors that fell from the heavens and that's why it was considered part of the sacred ceremony...

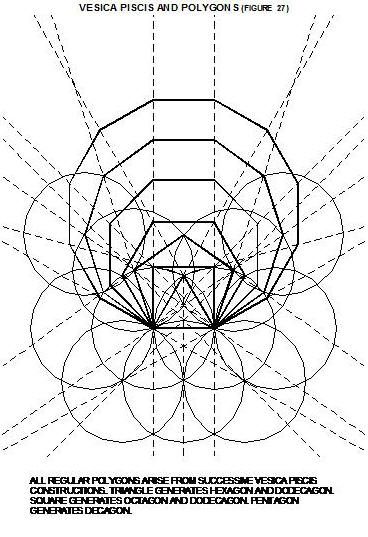
A Little Book of Coincidence by John Southcliffe Martineau


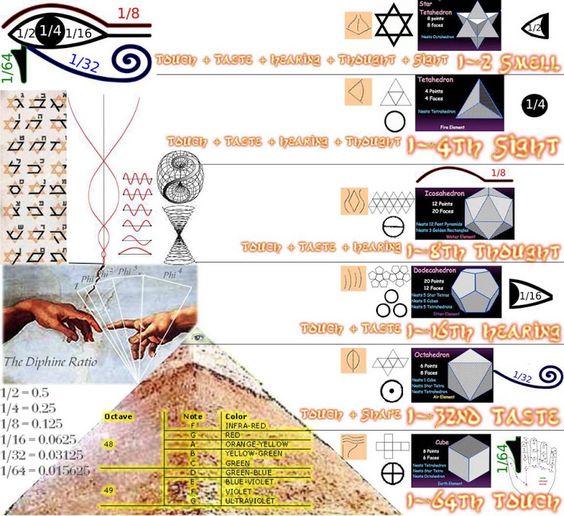
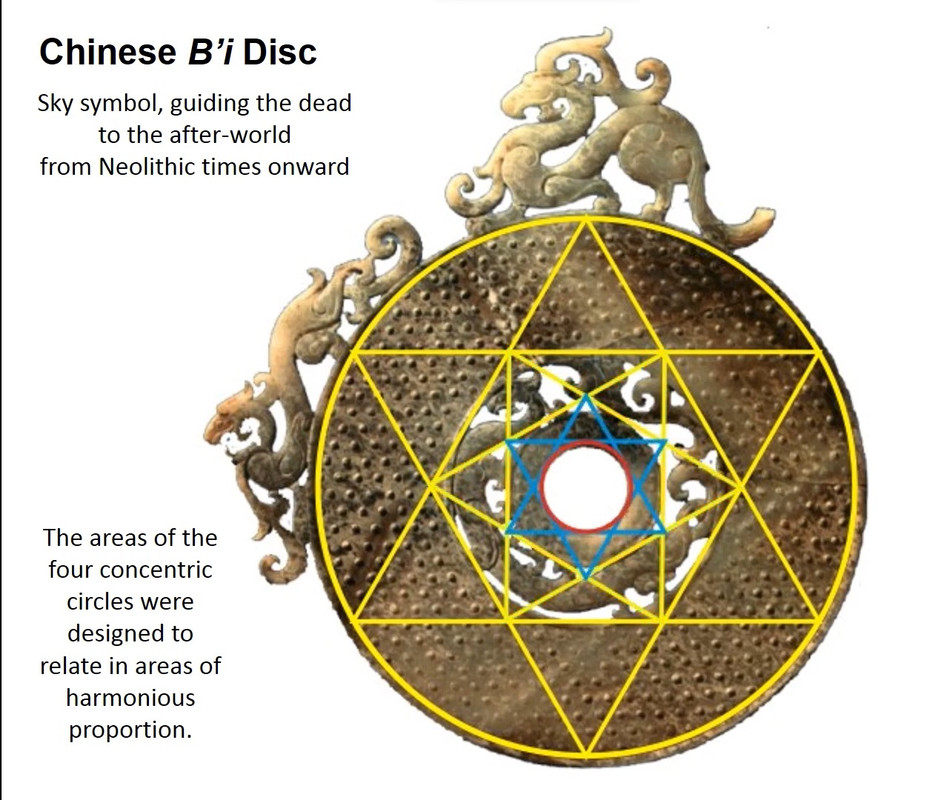

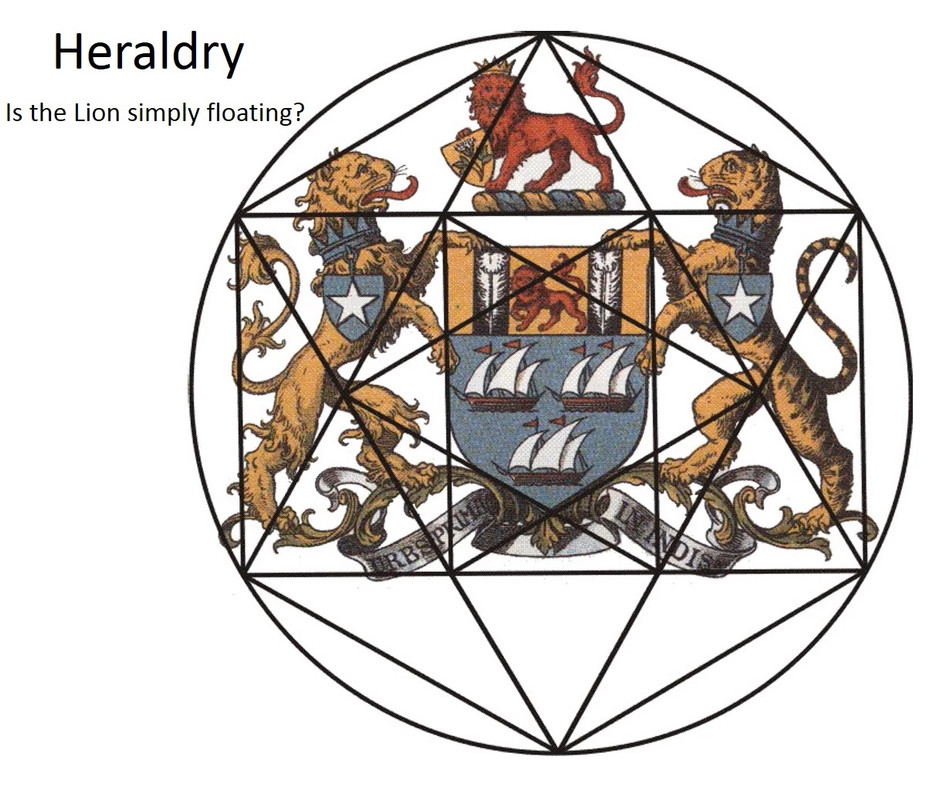
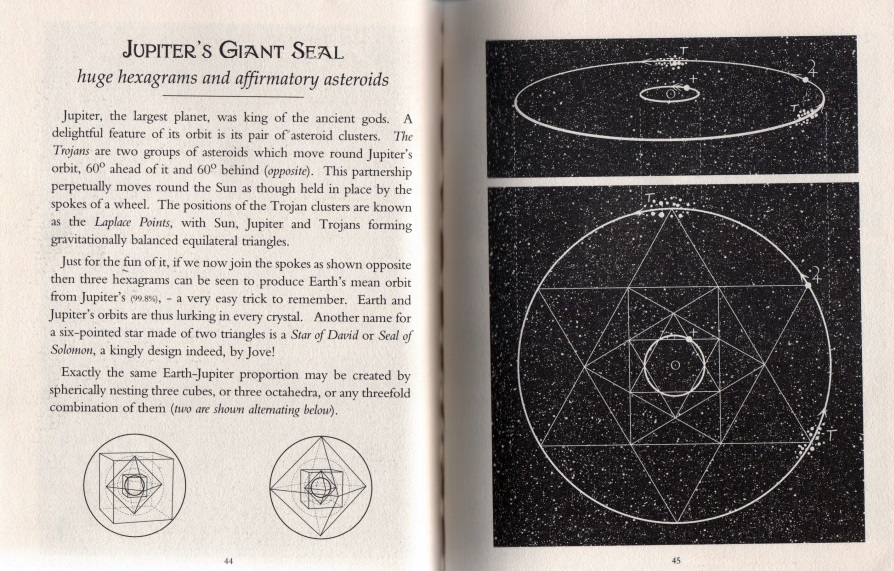
A Little Book of Coincidence by John Southcliffe Martineau
Unfolding from the Flower of Life

Further information and details:
Other videos of interest:
Aesthetic Ascent, Soul and Beauty- What if EYE got weirder? - explanation in above video, (also appears in Leonardo Da Vinci's Vitruvian man artwork):


Q Adam as the "Red Man" and the 32 Marks of the Great Man
Friday, January 2, 2015 Adam Was a Red Man by Alice C. Linsley The Biblical writers recognized that the people among the...

-
The spiritual meaning of dragonflies is the light of God. It also means looking within and dancing – just like a dragonfly. To a warr...
-
The Ennead or Great Ennead was a group of nine deities in Egyptian mythology worshiped at Heliopolis: the sun god Atum; his children S...